XMLwizard User Manual
- About XMLwizard
- A quick guide for the impatient
- Main screen
- The setup wizard
- Data import screen
- Data comparer
- Virtual columns
- Working with nested XML files
About XMLwizard
XMLwizard is a utility which can be used to load XML, CSV and flat textual files into Firebird databases. CSV is acronym for Comma Separated Values, but various forms of these files are supported (for example, TSV or Tab Separated Values), with user configurable delimiters, qualifiers and record separators. It supports multilevel XML files with unlimited depth of nesting.
Beside importing, XMLwizard has a powerful data comparer which can
be used to compare the data in input file against the data in the
database and show the difference in a grid. In this grid, user can
cherry-pick individual rows or even fields to be inserted, updated or
deleted from the database.
A quick guide for the impatient
- Run the program
- Let the wizard guide you through the setup of input file and target database
- Once you reach the main screen, select a table in the input file structure (tree control on the left) and click the Map to database button
- Select the table, columns and a primary key
- Click on Run data import and select whether you want to import the data or compare it against the database
- Select relevant options and click Start
If everything worked the way you wanted: Congratulations!
If not, read on...
Main screen
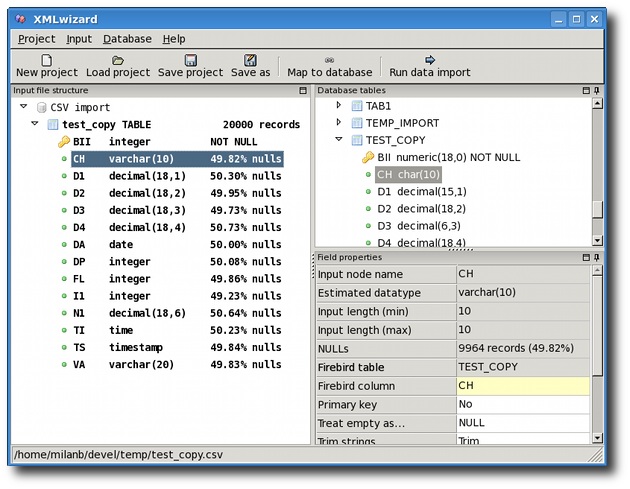
Main screen of XMLwizard has three sections. The main section on
the left contains a tree representing structure of the input file.
For each node, you can invoke the context menu do perform some
actions. When a node in the tree is selected, its detailed properties
are shown in the properties grid on the right-hand side. Some of the
values are read-only, while others can be set by typing directly in
the grid or selecting the value from a drop down list (fields marked
with yellow color). The third section contains a tree representing
structure of tables and columns in the target Firebird database.
The setup wizard
Once you start the program, a wizard is shown which will guide you
through selection of source input file and target database and
configuration of various options. If you cancel the wizard, you can
restart it at any time by selecting the New project option.
Database settings
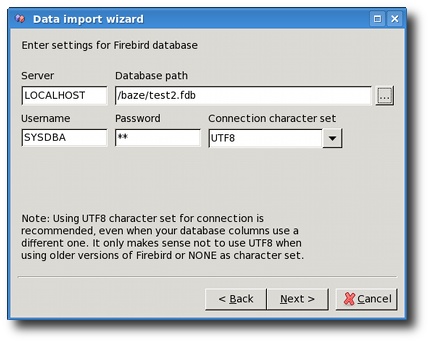
In the Server field you should enter the hostname or IP address of the Firebird server. If you are using Firebird embedded, leave the field blank.
In the Database path field you should enter the path to the Firebird database on the server, or an alias if you have set it up on Firebird server.
In fields Username and Password you should enter the user credentials.
In field Connection character set you can select some of the character sets offered in the dropdown list, or enter a completely new one. The reason for this is that some newer Firebird versions might support more character sets, and you wouldn't have to upgrade XMLwizard to a newer version just to have that working.
It is recommended that you use UTF8 character set for all
connections. The reason is that this character set simply works
out-of-the-box in most of the cases, because all other character sets
can be converted to it.
Input file settings
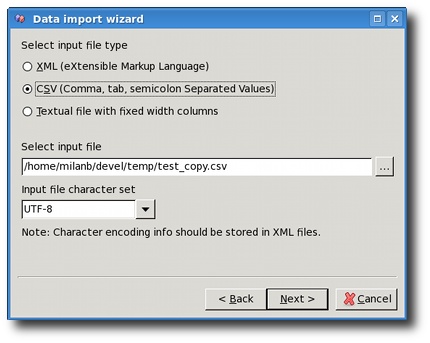
On this page you need to select the type of the input file and the file itself.
Please note that memory requirements for XML files are 10 times the size of the file, because the entire file with its structure and data is parsed and loaded by a DOM parser. This means that processing at later stage works much faster. For example, if you have some XML file of 20MB, XMLwizard's parser will require about 200MB of RAM to work properly.
If you are unsure which is the character set of the input file,
try with ISO8859_1 or UTF8. UTF8 is a superset of ASCII so it is
quite possible it will work. When loading XML files, the character
set option is disabled because character set information is stored in
XML files and the parser automatically detects it.
Common field settings
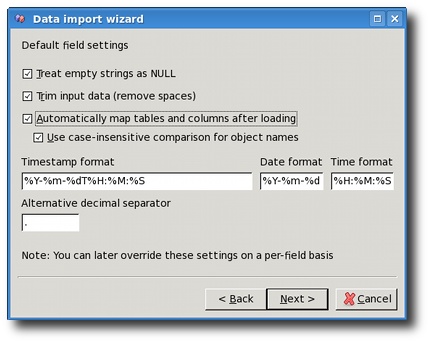
When the option Treat empty strings as NULL is checked XMLwizard will treat all the empty fields in the input as NULL. This setting is only relevant to fields of character types (char, varchar). With dates, times and numbers it is always on. For example, empty number field always defaults to NULL and not to zero.
Option Trim input data is also only relevant for character fields. For example, when strings are converted to numbers, the leading and trailing whitespace is ignored.
When option Automatically map tables and columns after loading
is checked, XMLwizard will look for node names in the input file
and try to automatically match those to the names of columns and
tables in the Firebird database. It uses table or column name for
matching, and you can control whether this matching will be case
sensitive or not. If you turn this option off, you can always invoke
this action using the option Map all automatically from the
Input menu in the main XMLwizard's window.
You can also
setup the default formats for date, time and timestamp columns. These
formats will be used while analyzing the input file to determine
whether some column is a date/time/timestamp column or not. If you,
for example, have different formats for the date fields in the same
input file, you can later modify the settings for each column
separately in the properties section of the main XMLwizard screen.
The date and time format uses placeholders to mark the place where a
value should be found. Those placeholders are prefixed with % sign,
and have the following meanings:
- a/A - short/full weekday name
- b/B - short/full month name
- y/Y - short/full year (2/4 digits)
- m - month 01-12
- d - day of month 01-31
- j - day of year 1-366
- w - day of week 0-6, 0 = sunday
- H - hour of day 00-23
- I - hour of day 01-12
- p - AM/PM mark
- M - minute 00-59
- S - second 00-59
- l - millisecond 000-999
- r - time in 12-hour format I:M:S p
- T - time in 24-hour format H:M:S
For example, to parse ISO date representation format (31st of December 2009 is represented as: 2009-12-31), we would use %Y-%m-%d format for dates.
The Alternative decimal separator setting is used when you
have (for example) numeric data with comma used as decimal separator
instead of dot (i.e. 123,45 instead of 123.45). This separator is
called Alternative because detection of values with dot as
decimal separator would still work properly even if you set the comma
as alternative separator.
Settings for CSV files
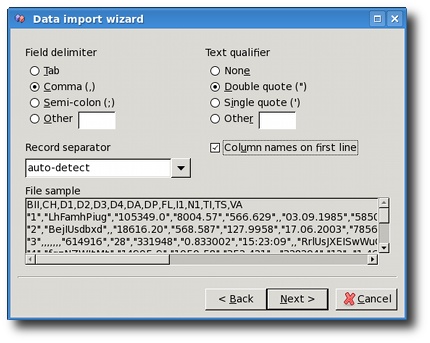
You can setup which characters are used as delimiter, which characters are used as record qualifiers and which characters are used as record separators. For example, if the CSV file looks like this:
"XMLWizard is here";98.50;"Finally!"
Then semi-colon is the field delimiter and double quote is the text qualifier.
CSV import also shows you a read-only preview of the first few
lines of the input file, so that you can easily spot which settings
to use. Please note that the preview does not change when you change
the settings. It always remains the same, showing the input file as
it is.
Settings for fixed-width textual files
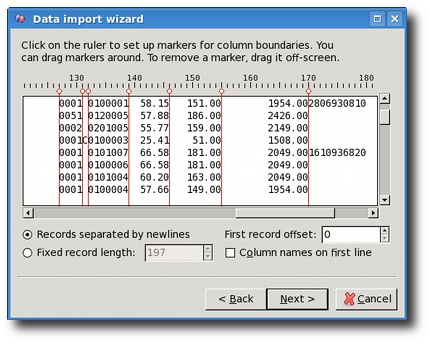
Importing flat textual files assumes that you either have a file that has a fixed record length, or that records are separated by newlines. The Fixed record length setting is in charcters, to avoid potential problems with variable length character sets like UTF-8. On the other hand, the First record offset setting is an offset of the first record from the start of the input file, and it is given in bytes. The reason for this is that you might have some file with a binary data in header which you might want to skip. Since it cannot be converted into characters there is no way to count them. A usual use case for this is when importing DBF files directly.
In the upper part of the screen you should setup the offsets of
each field in a record. Again, this works on character basis, and
WYSIWYG principle (what you see on the screen is what you get
imported in the database later). Note that one of the rows can be
marked if you click on it. This has no significant effect on the
import process, it's only visual aid used to help you when you have
really long lines in input file.
Check if input file is parsed correctly
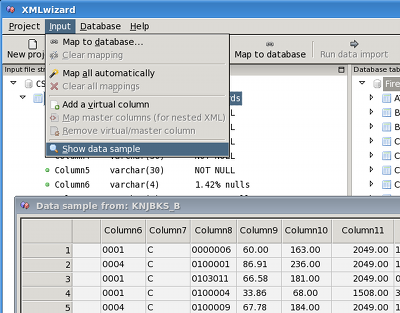
To check whether the file was loaded properly, you can always
preview the program's view of the data by selecting the Show sample
data option in the Input menu. Please note that this dialog
shows first 20 values found for each column. Therefore, if some of the
fields in input file are empty or not supplied (common in XML files),
this preview would not show the actual rows that would be inserted in
Firebird table.
Data import screen
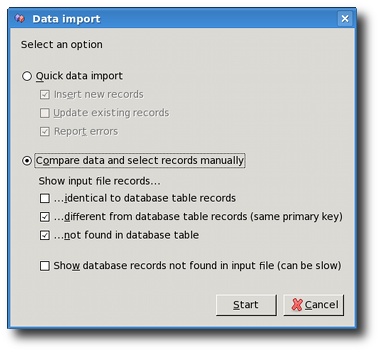
On this screen you should select whether you want to do quick data import into the database or you wish to compare the data. The quick data import only gives a progress bar and data is imported into the database without any prompting (except in case of errors). Many times, it is smart to first do the comparison to have a preview of what's going to happen.
Quick data import has three options:
- Insert new records - tries to insert records from the input file into the database
- Update existing records - tries to update an existing record in the database
- Report errors - you can disable error reporting completely
If both insert and update is selected then XMLwizard first tries to insert and if that fails it then tries to update without issuing an error. Therefore, selecting both options works like "overwrite" mode - adding new and updating the existing records in the database.
When error reporting is turned on, the import stops at every error
asking you what to do. However, you can decide to skip different
kinds of errors. It is always a good idea to start with error
reporting on, and turn some of the "expected" kinds of
errors off during the import. Of course, if you just want a quick and
dirty import for some testing purposes, it's easier just to ignore
all the errors and let it run.
When import is complete, the program will report number of records
that were successfully imported and ask you if you wish to commit the
transaction. So, you can still decide to abort if something has gone
wrong.
If you want to Compare data and select records manually you
need to select whether you want to see the records that are the same,
different (same primary key, but different values in some other
columns) or not found in database table (but present in the input
file).
All those options require a single scan of the input file. However,
the records are shown in the resulting grid in the order they are read
from the input file, so you might have a hard time finding, for
example, five new records in a pile of 10000 existing identical
records.
It's better to select to see only the new records in this case.
You can also select the option to see which records exist in
database, but are not present in the input file. This requires a full
scan of the database table, which is then checked against cache of
primary keys found in the input file. If you have a lot of records in
the database, this can be very slow, so it is turned off by default.
Data comparer
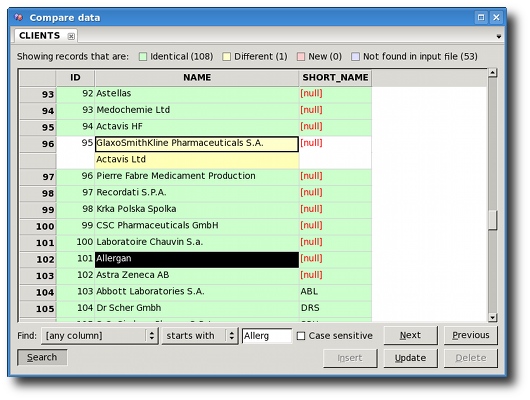
Data comparer loads all the data from the input file and checks
against Firebird database. If record has all the fields with the same
values, it is identical. If record has same values for primary
key column(s), it is different. If primary key is not found in
the database table, the record is new. Additionally, comparer
can read in all the records from database table and check that against
the input file to see which records are not found in the input file.
That option is off by default because it can work really slow if you
have a lot of records in the database.
On data comparer screen you can select individual cells in the table
to update the value in database with the value from file. Those fields
are marked with yellow color. The value in top row (light-yellow) is
the value from input file, while the value in bottom row (dark-yellow)
is the value from database. White cells mark the values that are same
in both input file and database, but are a part of row that has
different values. When all values are updated into database, both rows
will be removed from the grid automatically. You can hold down the Ctrl
key to mark multiple disconnected cells for update.
You can also use the Insert and Delete buttons to insert new (red)
cells, and delete rows from database table that are not found in the
input file (blue).
When multiple cells (or entire rows or columns) are selected the
Insert button would only insert new rows in that selection, Update
button would only update the different values in that selection, and
Delete button would only delete records not found in the input file.
Using the context menu, you can also copy the selected cells, and
paste them into some other program like text editor or a spreadsheet
(OpenOffice Calc, Microsoft Excel, etc.)
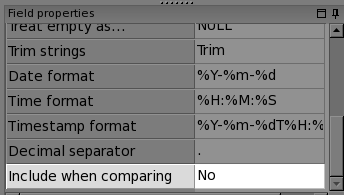
Tip: If, for some fields, you want only to see the values in the compare grid, but do not wish to consider the row as different, you need to set the Include when comparing option to No in the Field properties grid on the main program screen:
Virtual columns
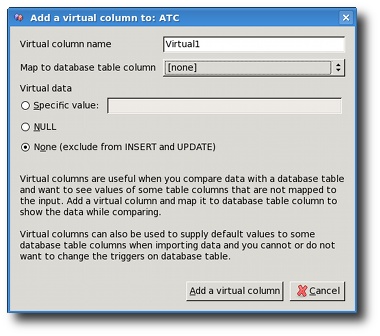
Virtual columns enable you to add a virtual column to your input file. While this column is not really a part of the input file, the engine will consider it as such. This enables you to provide defaults for some table columns and also to compare table columns against some fixed value. Here are the meanings of the virtual column settings:
Virtual column name is the name that will be used to display
the column in the input file structure tree on the left side of the
main screen. You can use any name you like.
Database table column mapping maps this virtual column to
some database table's column. This option is only enabled when the
parent input node is already mapped to some table. You can also set or
change this mapping later, after you add the virtual column.
Type of Virtual data can be a specific value, NULL
or None.
- Specific value can be something like "10", "abc", "2009-05-02", etc. The string you type is treated the same way as if it were extracted from the input file.
- NULL is treated like the field's value is not supplied in the input file.
- None is used when you want to see some table column's values in the compare dialog, but you don't want to use this virtual colunn while importing records.
When you create a virtual column having Specific value or NULL,
and you map it to the database table's column, that column will be set
to Specific value or NULL when records are imported.
Database column's values will also be compared against Specific
value or NULL when comparing data (unless you set Include
when comparing setting to No in field properties grid).
When you create a virtual column with data set up as None,
it will only be used when comparing. It would not compare database
column's data to anything, but rather just display it on the screen.
This is useful when you need some columns from database to have a
proper context while comparing, but those columns are not present in
the input file.
Working with nested XML files
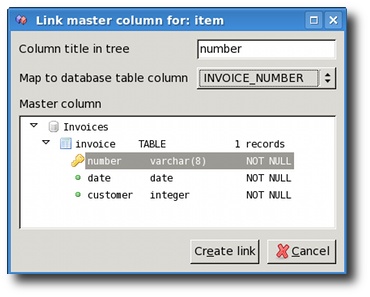
When working with nested XML files, it's a common requirement that
you need to use the value of some parent node's fields to insert in the
row in the database table mapped to the child node. This field is
usually a foreign key referencing the master table in master-detail
relationship, and it is called Master column in XMLwizard
terminology. Consider the following XML file structure and database
table structure:
<InvoicesDataset>
<invoice>
<number>329/2009</number>
<date>2009-04-20</date>
<customer>11234</customer>
<item>
<sku>6773</sku>
<price>12.89</price>
<quantity>18</quantity>
</item>
<item>
...etc.
</item>
</invoice>
</InvoicesDataset>
CREATE TABLE invoice_item (
invoice_number varchar(20) not null,
sku varchar(10) not null,
price decimal(18,2) not null,
quantity decimal(18,3) not null,
foreign key (invoice_number) references
invoice (number)
)
In the above example, invoice number is needed in order to insert
records into invoice_item table. However, since it is a nested XML
file, that data is not found at the same level. XMLwizard enables you
to create a link to any value which is above in the hierarchy by using Map
master columns option in the Input menu. You can also use
the context menu of the input tree node to get the same option.
In the above example, we would add a master column referencing
invoice number, so the engine will see a structure of the tree like
this:
<InvoicesDataset>
<invoice>
<number>329/2009</number>
<-------
<date>2009-04-20</date>
|
<customer>11234</customer>
|
<item>
|
<sku>6773</sku>
|
<price>12.89</price>
|
<quantity>18</quantity>
|
<invoice_number references="invoice.number" />
</item>
<item>
...etc.
</item>
</invoice>
<InvoicesDataset>
XMLwizard supports unlimited depth of nesting, so you can reference
fields that are more than one level up in the hierarchy.
 XMLWizard™
XMLWizard™